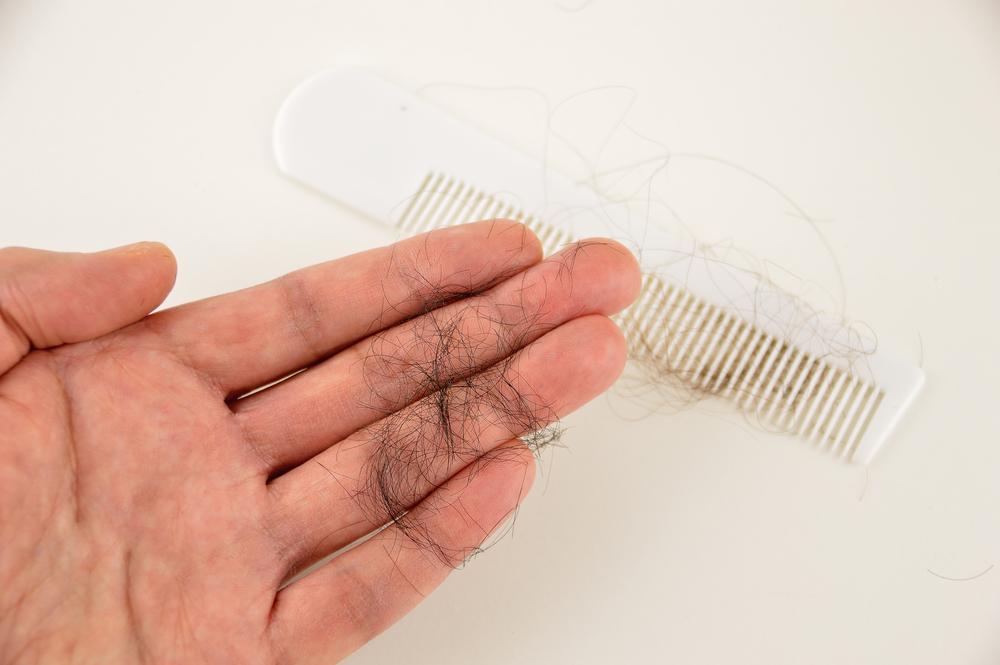
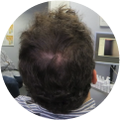
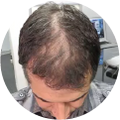
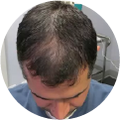
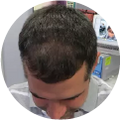
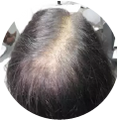
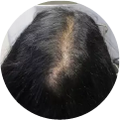
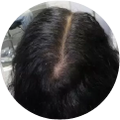
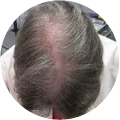
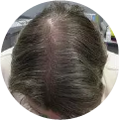
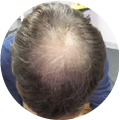
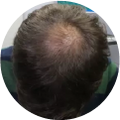
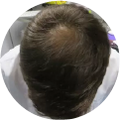
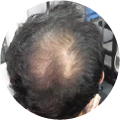
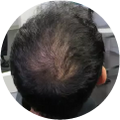
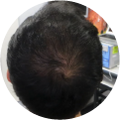
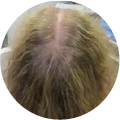
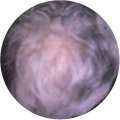
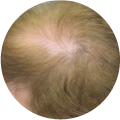
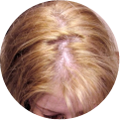
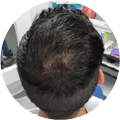
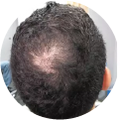
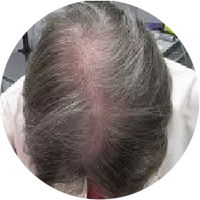
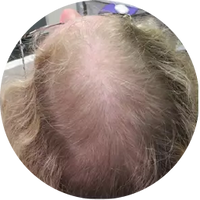
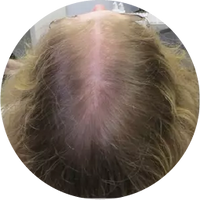
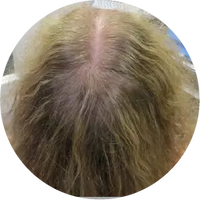
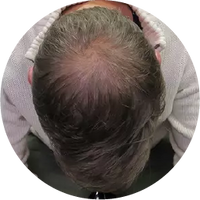
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common disorder occurring in the endocrine system that affects many women that are of reproductive age. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is characterized by many symptoms, but one of the most common results of this disorder is hair loss. If you are suffering from this disorder, you may be wondering how to reverse PCOS hair loss. Fortunately, there have been many cases of PCOS hair loss regrowth success.
PCOS hair regrowth is a process that requires commitment, research, and understanding to achieve success. PCOS hair loss regrowth is possible, but before you can successfully regrow lost hair you must understand what PCOS is, as well as how to combat PCOS and promote hair regrowth. Below is a guide of how to reverse hair loss due to PCOS.
Understanding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)

Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a unique disorder as its exact cause is unknown. For many, early diagnosis and treatment are the best treatments for preventing long-term complications. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is a common endocrine disorder and may result in infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods, obesity, acne, excess hair growth, and hair loss. When Polycystic Ovary Syndrome occurs in adolescents it is most often identified due to infrequent or absent menstruation. Women that are diagnosed with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome may possess enlarged ovaries that house small sacs of fluid, which are sometimes referred to as follicles, and which are most often identified during an ultrasound exam. For those suffering from obesity, weight loss has been shown to reduce the long-term effects of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, such as type 2 diabetes and heart disease.
Symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome

The symptoms associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome often begin occurring after a woman begins menstruating, which is referred to as menarche. There have been some cases of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome developing later in a woman’s reproductive life, though this most often occurs because of substantial weight gain. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome possesses a multitude of symptoms that may alert you or your physician to an issue. Each of these symptoms becomes increasingly pronounced in response to significant weight gain. However, though there are many commonly occurring symptoms, Polycystic Ovary Syndrome affects each woman differently and may manifest itself in a unique manner according to their unique genetic and environmental factors. Due to the large scope of manifestations of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, many physicians rely on identifying two of the below three symptoms to make a diagnosis.
- Irregular Periods: Irregular menstruation is the most common characteristic of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. The presence of irregular periods may range from menstrual intervals that exceed thirty-five days to fewer than eight menstrual cycles per year to prolonged periods that are excessively heavy in the flow. The manifestation depends entirely upon the person; however, despite this difference the presence of a significant irregularity is most often a sign of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Polycystic Ovaries: Polycystic ovaries are another common identifier of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Polycystic ovaries are enlarged and contain several small fluid-filled sacs that surround the eggs.
- Excess Androgen: The presence of elevated levels of Androgen, which is a male hormone, may result in physical signs that will point to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome as the cause. These symptoms may be excess facial and body hair, which is referred to as hirsutism, or male pattern baldness, which is referred to as androgenic alopecia. Another potential symptom of excess levels of Androgen is adult acne or severe adolescent acne.
Causes of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome

While the exact cause of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome remains a mystery, physicians have identified many factors that they believe play an active role in its occurrence. Hopefully in the near future medical professionals are able to pinpoint the exact cause of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome; however, until that time medical professionals rely on the preponderance of data gleaned from past cases to draw conclusions about contributing factors. Below are three factors commonly believed to play a role in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Heredity: As more cases of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome are examined, it has become a common belief that some element of this disorder stems from a heredity predisposition. In other words, if a female in your family, such as a mother or sister, suffers from Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, it is more likely that you also will be diagnosed with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. In addition, researchers are also working to identify if certain genes can be linked to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Excess Insulin: Insulin, which is sometimes referred to as blood sugar, is a hormone that is produced in the pancreas. Insulin allows cells to utilize glucose, which is also referred to commonly as sugar, to function as the body’s primary energy supply. When an individual possesses an insulin resistance, it means that their body’s ability to manufacture and utilize insulin effectively is compromised. In response to this insulin resistance, the pancreas must produce a higher output of insulin to make glucose available to the cells. Excess insulin has been linked to an increase in Androgen production, which researchers believe may interfere with the ovaries’ ability to ovulate.
- Low-Grade Inflammation: When the body detects an infection, the white blood cells present in your body react by producing substances to combat the infection, which is a response that is referred to as inflammation. In studies surrounding Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, research has shown that women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome possess low-grade inflammation. Low-grade inflammation of this type may stimulate polycystic ovaries to produce Androgens, leading to the symptoms outlined in the previous section.
Tips to Combat Hair Loss Caused by Polycystic Ovary Syndrome

While there is no one-size-fits-all solution to combatting hair loss caused by Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, there are many steps you can take to find the solutions that work best for your situation and symptoms. Below is a guide of various methodologies that have been shown to aid in reversing hair loss caused by Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Diet: Diet has a tremendous impact on health for everyone, but for those suffering from Polycystic Ovary Syndrome the impact is even more substantial. Obesity can greatly influence the severity of the symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, making it imperative for those with this condition to maintain a healthy weight. In addition, integrating a diet rich in foods that possess vitamins and nutrients known to increase hair growth and improve overall hair health will result in a more positive outcome. Due to the insulin resistance, sometimes present in manifestations of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, it is also recommended to incorporate a diet that has a low-glycemic index as this will result in steady blood sugar levels.
- Exercise: Another important tip to combatting hair loss caused by Polycystic Ovary Syndrome is exercise. Exercise reduces testosterone, which can be a culprit of hair loss as excess levels of testosterone increase the severity of some of the symptoms associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. In addition to this, cardiovascular exercise is also beneficial in treating this type of hair loss as it can counteract weight issues, which is a common symptom of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Stress Reduction: As with all types of hair loss, stress can play a significant role in hair loss as it throws your body into a state of panic and disrupts normal body processes. The presence of stress can lead to an increased level of cortisol, which is a hormone that has been known to increase the severity of hair loss. In addition to worsening hair loss, cortisol has also been known to lower immune function and bone density, increase weight, blood pressure, and cholesterol, and to interfere with learning and memory. To reduce stress, identify an activity that allows you to expend excess energy, requires you to completely focus on the task at hand, and that brings you a sense of peace upon completion. This activity can vary from yoga to surfing to reading to bird watching depending on the unique personality of the individual at hand, but identifying a way to reduce stress is critical to combatting hair loss caused by Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
- Implement a Consistent Eating and Sleeping Schedule:Lack of sleep results in a number of harmful consequences, which can ultimately worsen the symptoms and hair loss associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Sleep is regulated by serotonin and melatonin, both of which are hormones. When the levels of serotonin and melatonin are imbalanced, other hormones are also affected. For this reason, it is vital that you implement a steady sleep schedule and ensure you are getting enough sleep each night. In addition to this, eating regularly is an important step to combatting hair loss. By eating at regular intervals throughout the day, you will be able to maintain stable blood sugar levels, which prevents hormones from spikes and dips throughout the day. If you can successfully implement a consistent eating and sleeping schedule, you will prevent your hormones from being in a constant state of flux, which will lessen the symptoms of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, particularly hair loss.
- Develop a Routine to Care for Your Hair:This may seem self-explanatory, but many people suffering from hair loss do not take the necessary steps to take care of their hair in every possible facet. One of the most important things to consider when taking care of your hair is that what you use on your hair has a significant impact on its health. To reverse hair loss, it is important to invest in high-quality hair products that contain natural ingredients proven to promote hair regrowth. In addition, the use of heated styling tools and chemicals on hair can result in hair damage and hair loss, so be sure to limit the use of heated styling tools as much as possible, and always use a heat protectant if you use a heated styling tool. Avoiding chemicals, such as dyes and bleach, may seem impossible for some, but your hair will thank you for not subjecting it to the harsh irritants present in chemicals. In addition, some hairstyles can aggravate hair and increase hair shedding, such as tugging your hair back into a tightly wound bun or pulling it back into a tight ponytail. Be conscious of how you handle your hair and always remember to be gentle when maneuvering your locks.
- Oral Contraceptives:Oral contraceptives, also referred to as birth control pills are most often used to prevent pregnancy; however, birth control pills increase two female hormones in the body: progestin and estrogen. By increasing the levels of these two female hormones, it is possible to reduce hair loss and encourage hair regrowth. In addition to this, taking birth control pills also aids in making menstrual cycles more regular and reduces the level of Androgens produced by the ovaries, which can greatly help in reducing the symptoms associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Another symptom birth control pills aid in diminishing is the presence of acne, as the presence of regulated female hormones reduces breakouts and the appearance of acne. Always consult a doctor prior to beginning any type of oral contraceptive to make sure it does not interact with your current medications or have any harmful side effects.
- Do Not Smoke or Regularly Consume Alcohol:Smoking and the regular consumption of alcohol is never a healthy choice; however, with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome the consequences of these unhealthy habits are more pronounced. Smoking has been linked to over fifty different diseases, including lung cancer and heart disease, but studies have also shown that male pattern baldness and hair loss are linked to smoking. In addition, a study found that those who smoke twenty or more cigarettes a day more than double their risk of having moderate to severe hair loss than those who do not smoke. Smoking has also been showing to increase Androgen levels, which can have unwanted results for women.
- Use a Proven-Effective Solution: ScalpMed is a proven-effective regimen designed to treat hair loss and thinning hair. ScalpMed utilizes a uniquely developed two-step process to regrow hair. ScalpMed can halt and reverse heredity hair loss, and is also able to restore hair lost due to non-hereditary factors. ScalpMed was developed to give you back the hair you have lost and to restore your confidence in your hair.